8. Decreased bone mass
by Admin
Posted on 29-03-2023 04:41 PM
Low testosterone (also known as hypogonadism or low t) is an abnormally low level of testosterone in the blood. The testicles and adrenal glands produce testosterone in males. It’s an androgen , or male sex hormone, which is present from birth and is what makes a fetus male.
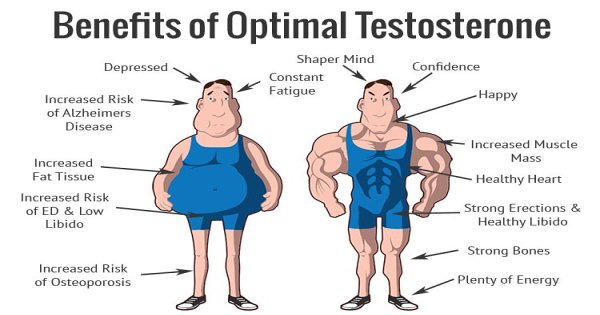
 During puberty, levels of testosterone surge, producing secondary sexual characteristics like muscle growth, body hair, and sperm production. And testosterone plays an essential role in people’s health throughout life, regulating libido , erectile function, sperm production, bone density, muscle mass, mood stability, and more ( nassar, 2022 ). Testosterone levels drop naturally with age, beginning in your 30s and 40s.
During puberty, levels of testosterone surge, producing secondary sexual characteristics like muscle growth, body hair, and sperm production. And testosterone plays an essential role in people’s health throughout life, regulating libido , erectile function, sperm production, bone density, muscle mass, mood stability, and more ( nassar, 2022 ). Testosterone levels drop naturally with age, beginning in your 30s and 40s.
Low energy/fatigue loss of muscle mass/reduced strength depression decreased or diminished libido/sex drive reduced bone density low red blood cell concentration the good news is that whatever the cause may be, hormone replacement therapy is here for you to bring your testosterone level back to an optimal range. We are always adding new patients to our wellness family. To get started with our hormone replacement program , we start with a simple blood draw. This will determine where your hormones are compared to the healthy range. Our providers then meet with you in a one-on-one consultation to discuss your symptoms and create a plan. Please fill out our online consultation form to start, and we will contact you to schedule the blood draw.
11. Smaller testicle and penis size
Without a steady flow of testosterone, the tissues in your penis, scrotum, and testicles can atrophy, or shrivel, says dr. Ramin. As a result, your penis might lose length and girth. You may notice your balls shrink, too—they often shrivel to half the size and turn squishy instead of firm, he says. Though testosterone replacement therapy won’t bring back your testicular volume, when it comes to your penis, the treatment “has a good chance of restoring its glory,” dr.
 Ramin says.
Ramin says.
One of the clearest ways to diagnose low testosterone is by testicle size. When testosterone levels are lower in the body, that can contribute to smaller testicles. Testicles are produced because of high testosterone levels in the body, so when those levels are decreased, it is natural for testicle size to decrease. In addition to a smaller testicle size, lower testosterone can also contribute to smaller penis size. There are other causes of smaller testicles, so smaller testicles cannot always necessarily be attributed to low testosterone.
Causes of low testosterone
Testosterone is the “male” hormone; it is responsible for the changes that occur in boys during puberty including deepening of the voice, growth of body hair, enlargement of the penis, development of muscle mass, and production of sperm. Testosterone plays an important role in adult men, specifically maintaining these biological functions and also playing a role in sexual function and libido. Low testosterone (sometimes referred to as hypogonadism) is the condition in which blood levels of testosterone are lower than expected. This can be due to certain medical conditions, stress, or problems with the pituitary gland or testicles that may be the result of certain congenital issues, infections, or treatments such as radiation or chemotherapy.
The "male menopause" (sometimes called the andropause) is an unhelpful term sometimes used in the media. This label is misleading because it suggests the symptoms are the result of a sudden drop in testosterone in middle age, similar to what occurs in the female menopause. This is not true. Although testosterone levels fall as men age, the decline is steady at about 1% a year from around the age of 30 to 40, and this is unlikely to cause any problems in itself. A testosterone deficiency that develops later in life, also known as late-onset hypogonadism, can sometimes be responsible for these symptoms, but in many cases the symptoms are nothing to do with hormones.
Testosterone levels naturally decrease as a man ages. The effects of gradually lowering testosterone levels as men age have received increasing attention in recent years. It is known as late-onset hypogonadism. After the age of 40, the concentration of circulating testosterone falls by about for most men. By the age of 60, the low levels of testosterone would lead to a diagnosis of hypogonadism in younger men. About 4 in 10 men have hypogonadism by the time they reach 45 years old. The number of cases in which older men have been diagnosed as having low testosterone increased 170 percent since 2012.